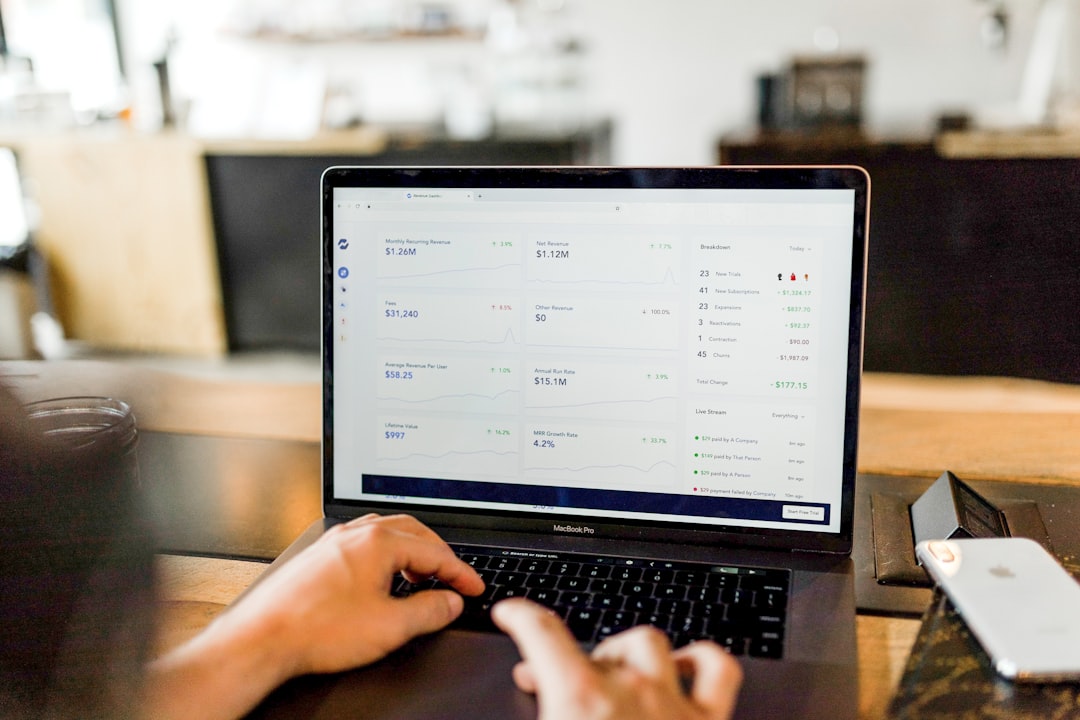
Data transparency refers to the practice of making data and information accessible and understandable to stakeholders. It is an essential aspect of decision-making as it allows individuals and organizations to make informed choices based on accurate and reliable information. In today’s data-driven world, where organizations collect and analyze vast amounts of data, transparency is crucial for ensuring that decisions are made with integrity and accountability.
Key Takeaways
- Data transparency is crucial for informed decision-making.
- Failing to explain data decisions can lead to mistrust and negative consequences.
- Effective communication strategies are necessary for stakeholders to understand data decisions.
- Balancing transparency with privacy concerns is important for ethical data practices.
- Building trust through transparent data practices can lead to organizational success.
The Importance of Data Transparency in Decision-Making
Data transparency plays a vital role in decision-making by providing individuals and organizations with the necessary information to make informed choices. When data is transparent, stakeholders can access and analyze it, enabling them to understand the underlying factors and make decisions based on evidence rather than assumptions or biases. This leads to more effective decision-making processes and better outcomes.
On the other hand, a lack of transparency can lead to poor decision-making. Without access to relevant data, stakeholders may rely on incomplete or inaccurate information, which can result in flawed decisions. For example, in the financial sector, the lack of transparency in mortgage-backed securities played a significant role in the 2008 financial crisis. Investors were unable to assess the risks associated with these complex financial products, leading to disastrous consequences.
The Risks of Failing to Explain Your Data Decisions
Failing to explain data decisions to stakeholders can have severe consequences for organizations. When decisions are made without proper explanation, stakeholders may feel excluded or mistrustful of the decision-making process. This can lead to a breakdown in communication and collaboration, hindering the organization’s ability to achieve its goals.
Furthermore, a lack of explanation can create confusion among stakeholders. Without understanding why a particular decision was made or how it was derived from the available data, stakeholders may question its validity or relevance. This can result in resistance or pushback against the decision, further complicating the implementation process.
Strategies for Communicating Data Decisions to Stakeholders
To effectively communicate data decisions to stakeholders, organizations should consider the following strategies:
1. Use simple, everyday language: Avoid technical jargon and complex terminology when explaining data decisions. Instead, use language that is easily understandable to a wide range of stakeholders. This will ensure that everyone can grasp the key points and implications of the decision.
2. Provide context: When explaining data decisions, it is essential to provide the necessary context for stakeholders to understand the decision-making process. This includes explaining the data sources, methodologies used, and any limitations or uncertainties associated with the data. By providing this context, stakeholders can better evaluate the decision and its potential impact.
3. Use visual aids: Visual aids, such as charts, graphs, and infographics, can be powerful tools for communicating complex data decisions. Visual representations make it easier for stakeholders to understand and interpret the information, enhancing their ability to make informed decisions.
Balancing Transparency with Data Privacy Concerns
While data transparency is crucial, organizations must also balance it with data privacy concerns. Protecting sensitive information is essential to maintain trust with stakeholders and comply with legal and ethical obligations. To strike a balance between transparency and privacy, organizations should:
1. Anonymize or aggregate data: When sharing data with stakeholders, organizations can anonymize or aggregate it to protect individual privacy. By removing personally identifiable information or combining data into broader categories, organizations can still provide valuable insights while safeguarding privacy.
2. Implement robust security measures: Organizations should invest in robust security measures to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or breaches. This includes encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to ensure that data remains secure.
3. Obtain informed consent: When collecting and using personal data, organizations should obtain informed consent from individuals. This means clearly explaining how their data will be used and giving them the option to opt out if they do not wish to participate.
Building Trust Through Transparent Data Practices
Transparent data practices can help build trust with stakeholders by demonstrating integrity, accountability, and a commitment to open and honest communication. When organizations are transparent about their data decisions, stakeholders are more likely to trust the information provided and have confidence in the decision-making process.
Transparency also increases credibility. When stakeholders can see the data and understand how decisions were made, they are more likely to view the organization as reliable and trustworthy. This can lead to stronger relationships, increased collaboration, and improved outcomes.
The Role of Data Visualization in Communicating Decisions
Data visualization is a powerful tool for communicating complex data decisions. By presenting data in a visual format, stakeholders can quickly grasp key insights and trends, making it easier for them to understand and interpret the information.
Effective data visualization techniques include using charts, graphs, maps, and infographics to present data in a clear and concise manner. Visual aids should be designed with the target audience in mind, using colors, shapes, and labels that are easily understandable and relatable.
How to Explain Complex Data Decisions to Non-Technical Audiences
Explaining complex data decisions to non-technical audiences can be challenging. To effectively communicate with this audience, organizations should:
1. Use relatable examples and analogies: When explaining complex concepts or processes, use relatable examples or analogies that non-technical audiences can understand. This helps bridge the gap between technical jargon and everyday experiences, making it easier for stakeholders to grasp the key points.
2. Break down information into digestible chunks: Complex data decisions can be overwhelming for non-technical audiences. Break down the information into smaller, digestible chunks that can be easily understood and absorbed. This allows stakeholders to focus on one concept at a time, increasing their comprehension and engagement.
3. Provide opportunities for questions and feedback: Encourage non-technical audiences to ask questions and provide feedback throughout the explanation process. This helps clarify any confusion or misconceptions and ensures that stakeholders feel heard and valued.
Incorporating Feedback and Input into Data-Driven Decisions
Incorporating feedback and input from stakeholders is essential for improving data-driven decisions. By actively seeking input, organizations can gain valuable insights, perspectives, and expertise that may have been overlooked in the initial decision-making process.
Feedback and input can help identify potential biases, blind spots, or limitations in the data or decision-making process. By addressing these issues, organizations can make more robust and informed decisions that are more likely to achieve desired outcomes.
The Benefits of Open Data and Transparent Decision-Making
Open data and transparent decision-making have numerous benefits for organizations and society as a whole. Some of these benefits include:
1. Increased innovation: When data is open and transparent, it can be accessed and used by a wide range of individuals and organizations. This promotes collaboration, knowledge sharing, and innovation, leading to new ideas, products, and services.
2. Improved accountability: Transparent decision-making holds organizations accountable for their actions and decisions. When stakeholders can see the data and understand how decisions were made, they can assess whether the organization is acting in their best interests and holding true to its values.
3. Enhanced public trust: Open data and transparent decision-making build public trust by demonstrating integrity, accountability, and a commitment to open and honest communication. This trust can lead to stronger relationships with stakeholders, increased support for organizational initiatives, and improved reputation.
Measuring the Impact of Transparent Data Practices on Organizational Success
Measuring the impact of transparent data practices on organizational success can be challenging but is essential for understanding the value of transparency. Some ways to measure this impact include:
1. Stakeholder surveys: Conducting surveys with stakeholders can provide valuable insights into their perceptions of transparency within the organization. Questions can focus on trust, credibility, satisfaction, and perceived value of transparent data practices.
2. Key performance indicators (KPIs): Identify KPIs that are directly or indirectly influenced by transparent data practices. For example, increased stakeholder engagement, improved decision-making outcomes, or reduced errors or inefficiencies can be indicators of the impact of transparency.
3. Case studies and success stories: Collect and share case studies and success stories that highlight the positive impact of transparent data practices. These real-life examples can demonstrate the value of transparency and its contribution to organizational success.
Data transparency is crucial for effective decision-making. It provides stakeholders with the necessary information to make informed choices, improves accountability and trust, and promotes collaboration and innovation. Organizations must prioritize transparent data practices by effectively communicating data decisions to stakeholders, balancing transparency with data privacy concerns, and incorporating feedback and input into decision-making processes. By doing so, organizations can reap the benefits of open data and transparent decision-making, leading to improved outcomes and organizational success.

